According to Financial Times;
“The real challenge for Muslim nations is economic.”
Financial Times
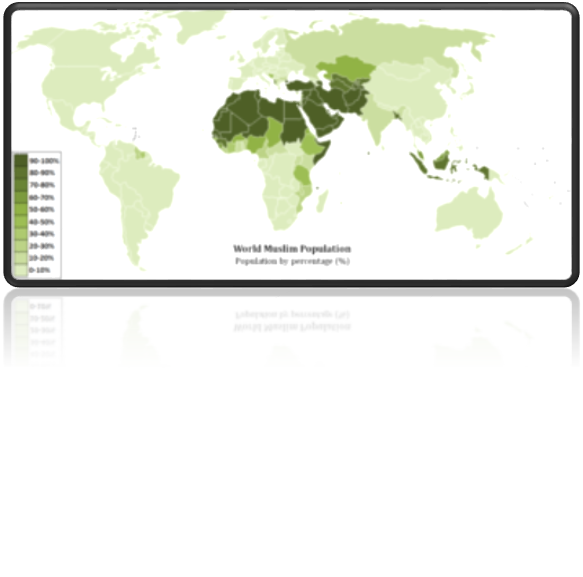
The Muslim Countries are 57 in number and a state (Palestine), according to OIC. As, majority of these Muslim Countries are in Asia and Africa. These countries are facing economic crisis excluding some which are oil rich. Some are under civil war and as a result their GDP, exports are crashed, their people are suffering from poverty, drought. Even Hundred thousands of people died in Muslim countries in the last three decades. Here, we will go through on economic crisis briefly in these countries.
The Concept of Islamic Economics:
Islamic economics refers to the knowledge of economics or economic activities and processes in terms of Islamic principles and teachings. Islam has a set of special moral norms and values about individual and social economic behavior. Therefore, it has its own economic system, which is based on its philosophical views and is compatible with the Islamic organization of other aspects of human behavior: social and political systems.
Objectives of Islamic Economic System:
Muslim economists have the consensus that the main objective of Islamic Economics is to establish social justice, elimination of poverty, tangible reduction in economic disparities, free society of corruption.
Economic Conditions of Islamic Countries:
The aggregate size of the economies of all Muslim countries put together is around $5.7 trillion — or 8.1% of the world total. The largest economy in the Islamic world is Indonesia with a size of $846 billion, followed by Turkey ($775bn) and Saudi Arabia ($577bn). Iran is the only other Muslim country with a GDP larger than $500bn.
Since 1980, the fastest-growing economies in the Muslim world have been Qatar (the size of whose economy has increased 22 times over this period), Oman (12 times), Malaysia (11.5 times), Turkey (11.3 times) , Indonesia (10.8 times) and Egypt (10.3 times). Pakistan has also been a relatively strong performer, with the size of its economy growing 8.9 times since 1980. By comparison, the world GDP grew by 6.4 times over this period.
The wealthiest Muslim countries in terms of per capita income (current US dollars) are Qatar, Kuwait and Brunei Darussalam. Their respective per capita incomes as of 2012 were $90,524, $56,514 and $41,127. Pakistan ranks 30th in per capita terms within the Muslim world.

Economic Crisis in Muslim Countries:
Middle East:
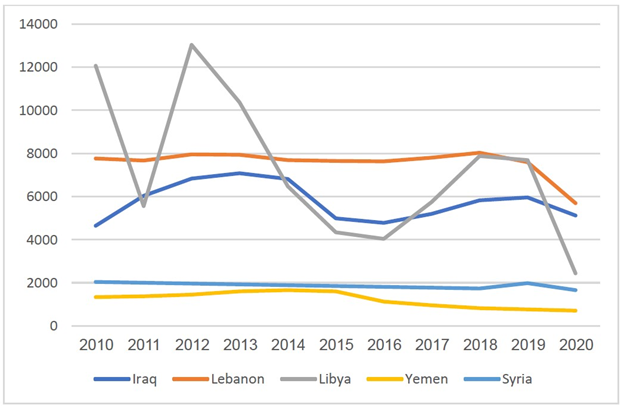
The economy of the Middle East is very diverse, with national economies ranging from hydrocarbon-exporting rentiers to centralized socialist economies and free-market economies. However, Lebanon, Syria, Iraq, Libya and Yemen are teetering on the brink of humanitarian catastrophe, with skyrocketing poverty and an economic implosion that threatens to throw the region into even deeper turmoil. There was a time not long ago when uprisings and wars in the Arab world topped the agenda at the U.N.
South Asia:
The problems of the oversupply of labor, unemployment, high illiteracy, a crisis in governance and threats to human security and poverty have also become increasingly serious. In addition, the rapid population growth has intensified the pressure on the food supply and worsened the average nutrition of the general public.
According to Canuto (2013), higher poverty rates and the large share of the poor in South Asia are driven mainly by region-wide political unrest. In fact, political tension and civil wars are common in most South Asian countries, meaning such turmoil reduces the effectiveness of a country’s anti-poverty policies.
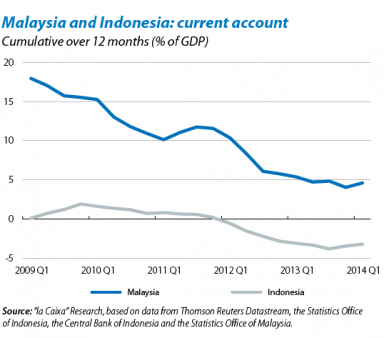
Malaysia and Indonesia (South East Asia):
One of the main reason of crisis in these countries is The Asian Financial Crisis is a crisis caused by the collapse of the currency exchange rate and hot money bubble. The financial crisis started in Thailand in July 1997 after the Thai baht plunged in value. It then swept over East and Southeast Asia.
Africa:
Terrorism, conflict resolution, border closures and immigration arbitrary borders created by the colonial powers, heterogeneous ethnic composition of African states, inept political leadership, corruption, negative effect of external debt burden and poverty among issues expected to continue to dominate continent. Since the mid-20th century, the Cold War and increased corruption, poor governance, disease and despotism have also contributed to Africa’s poor economy. According to The Economist, the most important factors are government corruption, political instability, socialist economics, and protectionist trade policy.
Conclusion:
From all these data, if peace is brought to the Islamic countries then there will be no power stopping them. if there will be a border free corridor, the economy of these countries can be boost. the belt road initiative, if extended to all Islamic countries one road concept then the crashed markets will rise up.
1 Comment
Abdullah Azeem · February 4, 2023 at 10:43 am
Great